slap tear test physiopedia|slap tear test shoulder : solution Superior labral tears (SLAP lesions) can pose a significant challenge to orthopaedic surgeons and rehabilitation specialists alike. Although advancement in arthroscopic techniques has enhanced arthroscopic repair of .
WEBPara fornecer as melhores experiências, usamos tecnologias como cookies para armazenar e/ou acessar informações do dispositivo. O consentimento para essas tecnologias nos permitirá processar dados como comportamento de navegação ou IDs exclusivos neste site.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Such slots also come with several other amazing bonus features. They range from wilds, scatters, free spins, and more. The most common 5-reel online casino slots for real money in the US include Mega Moolah, Starburst, National Lampoons Vacations, and Wolf Gold, to mention a few.
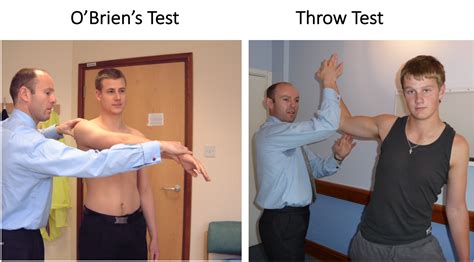
The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder .The Biceps Load II test is designed to detect SLAP lesions in the shoulder. [1] [2] Technique. Biceps Load II test technique. The patient is in the supine position with the shoulder in 120 degrees of elevation and full external rotation, while . The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint . A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and .
slap tear test shoulder
slap tear provocative test
Tears of the glenoid labrum fibrocartilage, also known as superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions, are suspected clinically or noted on magnetic resonance (MRI) . Superior labral tears (SLAP lesions) can pose a significant challenge to orthopaedic surgeons and rehabilitation specialists alike. Although advancement in arthroscopic techniques has enhanced arthroscopic repair of .
A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion.
A SLAP lesion is a type of shoulder injury that involves the labrum inside the shoulder joint. SLAP stands for Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior. It is most commonly found in athletes who do "overhead" sports, e.g. pitching, .
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .SLAP tears account for approximately 1% to 3% of injuries in sports medicine centres and approximately 6% of shoulder arthroscopy procedures show SLAP tears. Age variations: From the average age of 35, the superior labrum is less firmly attached to the glenoid than in people under the age of 30. A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Yergason's Test is used to test for biceps tendon pathology, such as bicipital tendonitis and an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesion.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patient should be seated or standing in the anatomical position, with the .
Positive Test [edit | edit source]. Clunk or Grinding: A clunking or grinding sensation is felt or heard, indicating a possible labral tear. Pain: The presence of pain during the maneuver can also indicate a positive test. Significance [edit | edit source]. Labral Tear: The test is particularly useful for identifying superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions.Proximal biceps tendinopathy is the inflammation of the tendon around the long head of the biceps muscle.. Biceps tendinitus can impair patients' ability to perform many routine activities. Main function of the biceps muscle is forearm supination and elbow flexion.; Biceps also contribute 10 percent of the total power in shoulder abduction when the arm is in external . Superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions constitute a recognized clinical subset of complex shoulder pain pathologies. SLAP lesions demonstrate a predilection for young laborers, overhead athletes, and middle-aged manual laborers.[1] In 1985, Andrews first described superior labral pathologies, and Snyder later coined the term “SLAP lesion” because of the .A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. . Sometimes, a special type of MRI, called an MRI arthrogram, is needed to see the SLAP tear. This test is .
Labral injuries are named according to their location: Superior labrum: SLAP lesions are the most common and includes 8 types of SLAP tears. Less frequently, Andrew's lesion can occur.; Anterior labral tear: This is very rare and is a pure anterior tear associated with a medial glenohumeral ligament tear.; Posterior labrum: Less frequent when compared to anterior tears.SLAPprehension Test. Jo Gibson. This test was described by Berg and Ciullo in 1998 and was developed after 2 patients described cervical spine and shoulder pain and a click associated with turning a steering wheel Le. horizontal flexion and internal rotation after RTA. Arthroscopy revealed the presence of a type II SLAP lesion in both patients.. Test. The patient is examined .Definition/Description [edit | edit source]. An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint.For example, a tear could decrease the acetabular contact .
slap tear physical exam
A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. . Sometimes, a special type of MRI, called an MRI arthrogram, is needed to see the SLAP tear. This test is .
SLAP Lesion Cluster 1 | Shoulder Assessment. According to a study done by Schlechter et al. (2009), a combination of the Active Compression Test and the Passive Distraction test yields a positive likelihood ratio of 7.0 for 2 positive tests and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.33 for two negative tests. This test cluster therefore has moderate clinical value to confirm or rule out .The Dynamic Labral Shear Test is an orthopedic test to assess for SLAP lesions / the superior biceps labrum complex in the shoulder. According to a study done by Sodha et al. (2017) , the dynamic labral shear test has a sensitivity of 78% and a specificity of 51% in isolated SLAP lesions and a lower sensitivity of 57% and a specificity of 52% .
Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . SLAP or labral lesions; Acromioclavicular Joint Disorders; Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder) . The following additional test should also be used to rule out a Rotator Cuff Tear; Drop Arm Test: To test .
Description [edit | edit source]. A Hill-Sachs lesion is an osseous defect or "dent" of the postero-supero-lateral humeral head that occurs in association with anterior instability or dislocation of the glenohumeral joint. It is often associated with a .Test Item Cluster: When this test is combined as a cluster with the Painful Arc Sign and the Infraspinatus test, and all three tests report a positive, then the positive likelihood ratio is 10.56 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is .17. If two of the three tests are positive, .In 2017, Somerville et al. assessed the diagnostic accuracy of physical examination tests to diagnose SLAP tears. Among others, the Biceps Load 1 test was included based on surgeon preference. . and specificity or 87,5% which translates to rather poor likelihood ratios and which is why the clinical value of this test to assess SLAP lesions is .Bankart lesions are injuries of the anteroinferior aspect of the glenoid labral complex and are often found in association with a Hill-Sachs lesion.This injury is a common complication of anterior shoulder dislocation and/or repeated anterior shoulder subluxations. The dislocation of the shoulder joint (anterior) can damage the connective tissue ring around the glenoid labrum.
Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . Glenoid labrum tear : Slap lesion, Bankart lesion; Cervical pathology: Cervical nerve root injury, . To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed.Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Passive Compression Test is a provocation test used to determine if there is a Superior Labral Anterior Posterior(SLAP) lesion.This maneuver involves passive external rotation and compressing the humeral head onto the glenoid, hence it is named the "passive compression test.". Technique [edit | edit source]. The test is performed with .In the study, MRIs from patients between 51-65 were twice as likely to show a SLAP tear and in patients older than 65 the chance of a SLAP tear increased fourfold compared to 35-50 years of age. On the other hand, . and/or a negative palpation test (Sensitivity: 92-98%/ Specificity: 52-73) are helpful in the exclusion of lesions to the biceps . What is a SLAP tear? SLAP stands for "superior labrum from anterior to posterior." This type of shoulder labral tear occurs at the top (“superior”) of the glenoid labrum where it connects to the biceps tendon, and it extends in a curve from the chest (“anterior”) to the back (“posterior”).
Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . To test for the presence of subacromial impingement. Tests for Subacromial Impingement . Drop-arm sign, Infraspinatus muscle test positive the +LR: 15.57 of full thickness rotator cuff tear If Hawkins .They reported a sensitivity and specificity of 75.5% and 85% respectively, meaning a negative test is extremely accurate in ruling out posterior rotator cuff tears. A (+) test is indicated by the presence of deep posterior shoulder pain when the arm is brought into a position of abduction to 90° to 110°, extension to 10° to 15°, and maximal . A SLAP tear is a type of shoulder injury. It affects the labrum, which is the cartilage in the shoulder’s socket. Here's what you need to know about causes, treatments, and recovery.Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Apprehension test is generally used to test the integrity of the glenohumeral joint capsule, or to assess glenohumeral instability in an anterior direction.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patient should be position in supine. The therapist will flex the patient's elbow to 90 degrees and abducts the patient's shoulder to 90 degrees in sagittal .
Assistir a Tinker Bell: O Segredo das Fadas | Disney+. Tinker Bell atravessa o Bosque do Inverno proibido e descobre que tem uma irmã.
slap tear test physiopedia|slap tear test shoulder